RET Reactor Green Energy

Growing populations, rising standards of living, and increasing urbanization are contributing factors driving expanding volumes of MSW and biomass. MSW is defined as household waste, commercial solid waste, non-hazardous sludge, and some industrial solid waste. The large amounts of MSW that are hauled to landfills have become a major environmental issue throughout the world. Landfills in the US, Europe and almost elsewhere are nearing capacity, and the ability to add capacity is hindered by budget restraints, stringent environmental regulations, and lack of available space.
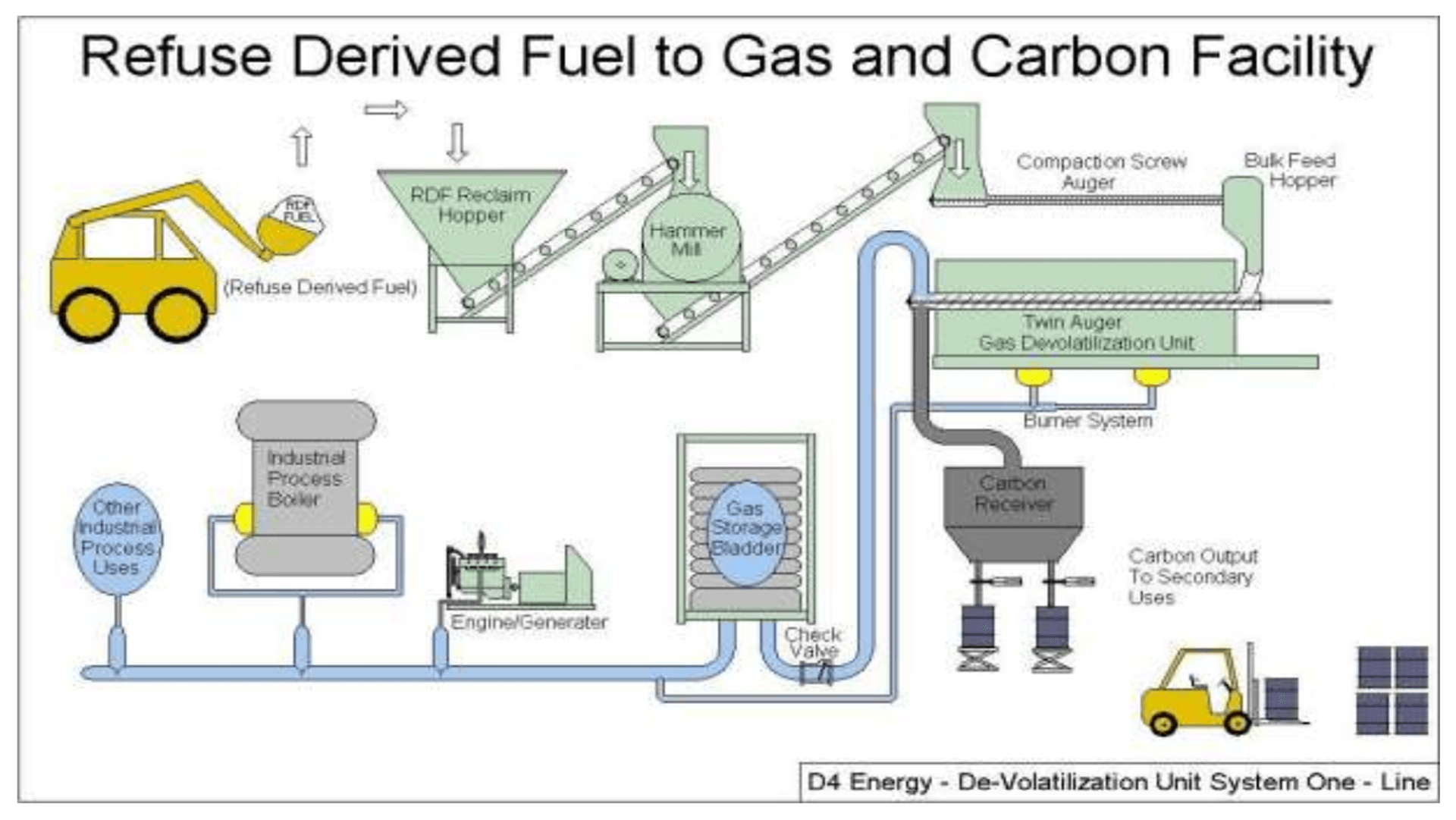
Both public and private sector entitles are increasingly looking to WtE technologies as an answer to these problems. WtE is an umbrella name for technologies that are used to create energy out of waste. WtE systems convert a carbon-based waste stream into a usable form of energy (syngas, electricity, heat, etc.). WtE installations serve a dual purpose. First, they help alleviate the growing MSW problem. Second, they provide a much-needed source of renewable energy while simultaneously reducing the amount of greenhouse gasses released into the atmosphere.
INPUTS OUTPUTS
1. Hazardous Material 1. Fertilizer
2. MSW General Waste 2. Heating
3. Biomass 3. Dimethyl Ether / Methanol / Ethanol
4. Animal Manure 4. Soil Enhancements
5. Tires 5. Biochar
6. Diesel
7. Heavy Fuel Oil
8. Gasoline
9. Power Generation (Electricity)
10.Water